El Niño and La Niña Understanding the Oceanic Phenomena
El Niño and La Niña Understanding the Oceanic Phenomena – El Niño and La Niña are two of the most significant oceanic phenomena that influence global weather patterns, impacting climates, ecosystems, and economies around the world. In this article, we explore the dynamics of El Niño and La Niña, their effects on weather systems, and their implications for various regions.
Understanding El Niño and La Niña:
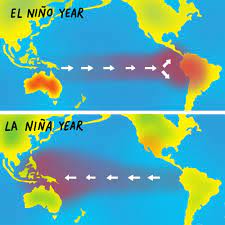
El Niño and La Niña are opposite phases of the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) cycle, a natural climate phenomenon that occurs in the equatorial Pacific Ocean. El Niño refers to the warm phase of the ENSO cycle, characterized by unusually warm sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern Pacific, while La Niña represents the cool phase, marked by cooler-than-average sea surface temperatures in the same region.
El Niño Events:
During El Niño events, warm oceanic waters in the central and eastern Pacific Ocean disrupt normal atmospheric circulation patterns, leading to changes in weather patterns around the globe. El Niño typically brings above-average rainfall to the western Pacific and drought conditions to the western coast of South America, leading to floods, landslides, and agricultural disruptions.
La Niña Events:
Conversely, La Niña events are associated with cooler-than-average sea surface temperatures in the equatorial Pacific, which can intensify normal atmospheric circulation patterns. La Niña often results in increased rainfall in the western Pacific and drier conditions in the western United States and South America, leading to floods, hurricanes, and agricultural losses.
Impacts on Weather Systems:
El Niño and La Niña events can have far-reaching effects on weather systems across the globe. They influence the position and intensity of the jet stream, which in turn affects the distribution of rainfall, temperature patterns, and storm tracks. These phenomena can lead to extreme weather events such as droughts, heatwaves, floods, and hurricanes in various regions.
Regional Implications:
The impacts of El Niño and La Niña vary by region, depending on factors such as geography, topography, and local climate conditions. In some areas, El Niño events may bring much-needed rainfall and alleviate drought conditions, while in others, they can lead to devastating floods and crop failures. Similarly, La Niña events can result in beneficial rainfall for agricultural regions or exacerbate drought conditions and water shortages.
Predictability and Forecasting:
Efforts to predict El Niño and La Niña events have improved in recent years, thanks to advancements in climate modeling and ocean monitoring technologies. Forecasting agencies use a combination of statistical models, computer simulations, and observations of oceanic and atmospheric conditions to anticipate the onset, intensity, and duration of ENSO events, providing valuable information for disaster preparedness and resource management.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, El Niño and La Niña are complex oceanic phenomena that play a significant role in shaping global weather patterns and influencing regional climates. By understanding the dynamics of these phenomena and their impacts on weather systems, communities, governments, and businesses can better prepare for and mitigate the effects of extreme weather events associated with El Niño and La Niña, ensuring resilience and sustainability in an ever-changing climate.
