Insights into the Frigid Air Masses the Arctic and Antarctic
Insights into the Frigid Air Masses the Arctic and Antarctic – The Arctic and Antarctic regions are characterized by extreme cold temperatures, vast expanses of ice, and unique weather phenomena that play a significant role in shaping global climate patterns. In this article, we delve into the frigid air masses of the Arctic and Antarctic, exploring their characteristics, impacts, and insights into polar weather patterns.
Understanding Polar Air Masses:
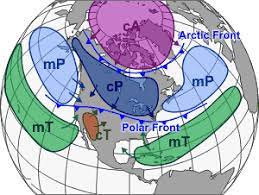
Polar air masses originate from the high latitudes of the Earth’s polar regions, where temperatures are consistently cold year-round. These air masses are characterized by their low temperatures, low humidity levels, and stable atmospheric conditions. As polar air masses move away from the poles and interact with warmer air masses, they can influence weather patterns and climate conditions in other regions of the world.
Arctic Air Masses:
Arctic air masses originate from the Arctic region, encompassing the North Pole and surrounding areas. These air masses are extremely cold and dry, with temperatures often plunging well below freezing. Arctic air masses can bring bitterly cold temperatures, strong winds, and snowfall to regions in North America, Europe, and Asia during the winter months, leading to frigid conditions and hazardous weather events.
Antarctic Air Masses:
Antarctic air masses originate from the Antarctic continent and surrounding Southern Ocean. Similar to Arctic air masses, Antarctic air masses are characterized by their extreme cold temperatures and low humidity levels. During the austral winter, these air masses can influence weather patterns in southern South America, Australia, and New Zealand, bringing cold fronts, strong winds, and precipitation to these regions.
Impacts on Weather Patterns:
The movement of polar air masses can have significant impacts on weather patterns and climate conditions around the world. When polar air masses collide with warmer air masses, they can trigger the formation of frontal systems, including cold fronts and occluded fronts, leading to changes in temperature, precipitation, and atmospheric instability. Polar air masses can also influence the formation of storm systems, such as nor’easters in North America and blizzards in Europe, contributing to extreme weather events.
Insights into Polar Weather Patterns:
Studying polar air masses provides valuable insights into the dynamics of polar weather patterns and their interactions with other atmospheric phenomena. Scientists use advanced observation techniques, such as satellite imagery, weather balloons, and computer models, to monitor polar air masses and track their movement across the globe. By understanding the behavior of polar air masses, meteorologists can improve weather forecasting accuracy and provide early warnings for hazardous weather conditions.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, insights into the frigid air masses of the Arctic and Antarctic are essential for understanding polar weather patterns and their impacts on global climate systems. By studying the characteristics, movement, and interactions of polar air masses, scientists can gain valuable insights into the dynamics of polar weather and improve our ability to forecast and mitigate the impacts of extreme weather events. As climate change continues to affect polar regions, understanding polar air masses becomes increasingly important for addressing the challenges of a changing climate and ensuring the resilience of communities around the world.
